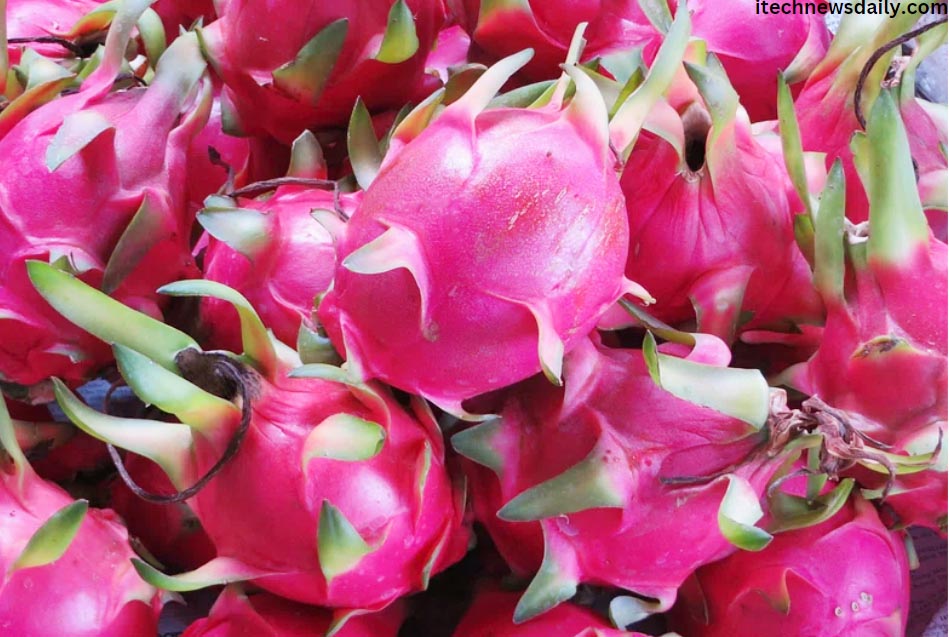
Dragon fruit, also known as pitaya or pitahaya, is a visually stunning and nutritionally rich fruit that has gained immense popularity in recent years. With its vibrant colors, unique appearance, and a plethora of health benefits, dragon fruit has become a favorite among fruit enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike. One common question that arises among consumers is, “When is dragon fruit in season?” In this comprehensive guide, we will delve in the various factors that influence dragon fruits seasons, the different varieties available, and the best time to enjoy this exotic fruit.
Understanding Dragon Fruit:
Before we delve into the seasonal aspects, let’s take a moment to understand dragon fruit itself. The dragon fruit plant belongs to the cactus family, specifically the genus Hylocereus. The fruit is characterized by its vibrant pink or yellow outer skin, adorned with green scales or spines, and a sweet, mildly flavored inner flesh speckled with tiny black seeds.
Dragon fruit comes in several varieties, with the most common being the Hylocereus undatus (white-fleshed pitaya) and Hylocereus polyrhizus (red-fleshed pitaya). The white-fleshed variety typically has a sweeter taste, while the red-fleshed variety is known for its slightly earthier flavor. Additionally, there is the yellow dragon fruit, which is less common but equally delightful.
Factors Influencing Dragon Fruit Seasons:
Several factors influence the seasonality of dragon fruit, including climate, geographical location, and the specific variety of dragon fruit being cultivated. Let’s explore these factors in detail:
Climate:
- Dragon fruit thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. It is sensitive to cold temperatures, and frost can damage or kill the plant. The ideal temperature range for dragon fruit cultivation is between 65°F to 100°F (18°C to 38°C). In areas with consistent warm temperatures, the plant can bear fruit year-round.
Geographical Location:
- The geographical location of dragon fruit farms plays a crucial role in determining the fruit’s seasonality. In countries with tropical climates, such as Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines, dragon fruit may be available throughout the year. In contrast, regions with distinct seasons, like the United States or parts of Europe, might experience a more defined dragon fruit season.
Variety of Dragon Fruit:
- Different varieties of dragon fruit may have varying growing seasons. While some varieties may produce fruit year-round, others might have more specific periods of peak production. Understanding the specific variety of dragon fruit being cultivated is essential for determining when it is in season in a particular region.
When is Dragon Fruit in Season?
Now that we have a better understanding of the factors influencing dragon fruit seasons, let’s explore when you can typically find this exotic fruit at its best:
Year-Round Availability in Tropical Regions:
- In tropical regions like Southeast Asia, where dragon fruit is native, the fruit can be available year-round. Countries such as Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines boast favorable climates for continuous dragon fruit cultivation, allowing consumers to enjoy the fruit’s freshness at any time.
Seasonal Availability in Subtropical Regions:
- Subtropical regions, including parts of the United States (such as Florida, California, and Texas), may experience seasonal availability of dragon fruit. In these areas, the fruit is more likely to be in season during the warmer months, typically from late spring to early fall, when temperatures are conducive to fruiting.
Greenhouse Cultivation:
- In regions with colder climates or distinct seasons, greenhouse cultivation has become a popular method to extend the availability of dragon fruit. Greenhouses provide controlled environments that mimic the tropical conditions necessary for dragon fruit cultivation. This allows farmers to produce the fruit year-round, regardless of external weather conditions.
Varieties of Dragon Fruit and Their Seasons:
Different varieties of dragon fruit may exhibit variations in their growing seasons. Let’s take a closer look at some common dragon fruit varieties and their respective seasons:
Hylocereus Undatus (White-Fleshed Pitaya):
-
-
- This variety is known for its sweet and mildly tangy flavor.
- In tropical regions, it may be available year-round.
- In subtropical regions, peak seasons typically align with warmer months.
-
Hylocereus Polyrhizus (Red-Fleshed Pitaya):
-
-
- The red-fleshed dragon fruit variety has a slightly earthier taste compared to the white-fleshed variety.
- Availability may follow a similar pattern to the white-fleshed variety, with year-round availability in tropical regions and seasonal availability in subtropical regions.
-
Yellow Dragon Fruit:
-
- Less common than its pink-skinned counterparts, yellow dragon fruit has a sweet and milder taste.
- Availability may vary, but it generally follows the patterns of other dragon fruit varieties in terms of seasonality.
Cultivation Practices and Harvesting:
Successful dragon fruit cultivation involves specific practices to ensure optimal fruit production. Here are key aspects of dragon fruit cultivation and harvesting:
Soil and Planting:
-
-
- Dragon fruit plants prefer well-draining soil, and they are often grown in sandy or loamy soil types.
- Planting typically occurs in raised beds or mounds to facilitate proper drainage.
-
Temperature and Sunlight:
-
-
- Dragon fruit plants thrive in full sunlight.
- Warm temperatures, with minimal exposure to frost, are crucial for healthy plant growth and fruit production.
-
Irrigation:
-
-
- Dragon fruit plants require regular watering, especially during dry periods.
- Overwatering should be avoided to prevent root rot.
-
Support Structures:
-
-
- As the dragon fruit plant grows, it needs support structures such as trellises or stakes to prevent sprawling and enhance air circulation.
-
Pollination:
-
-
- Dragon fruit is primarily pollinated by nocturnal pollinators such as bats and moths.
- Some varieties are self-pollinating, while others benefit from cross-pollination for optimal fruit set.
-
Harvesting:
-
- Dragon fruit is typically ready for harvest 30 to 50 days after flowering.
- Harvesting is done by hand, and the fruit should be picked when fully ripe for the best flavor and texture.
Dragon Fruit Around the World:
Let’s explore how dragon fruit is cultivated and enjoyed in various regions around the world:
Southeast Asia:
-
-
- Dragon fruit is native to countries like Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines.
- In these regions, it is a staple fruit with year-round availability.
-
United States:
-
-
- In the U.S., dragon fruit cultivation is prominent in states with warmer climates, such as California, Florida, and Texas.
- Greenhouse cultivation has extended the availability of dragon fruit in other regions.
-
Central and South America:
-
-
- Countries like Mexico and Colombia are significant producers of dragon fruit.
- Similar to Southeast Asia, dragon fruit is a popular fruit with continuous availability.
-
Australia:
-
- In Australia, dragon fruit cultivation is gaining popularity in northern regions with tropical and subtropical climates.
- Local production contributes to the availability of the fruit.
Health Benefits of Dragon Fruit:
Dragon fruit is not only visually appealing but also packed with essential nutrients and health benefits. Here are some reasons why adding dragon fruit to your diet can be advantageous:
Rich in Antioxidants:
-
-
- Dragon fruit is loaded with antioxidants, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
-
Vitamins and Minerals:
-
-
- It is a good source of vitamins such as vitamin C, vitamin B, and essential minerals like iron and magnesium.
-
Dietary Fiber:
-
-
- The high fiber content in dragon fruit aids digestion and promotes a healthy gut.
-
Hydration:
-
-
- Dragon fruit has a high water content, contributing to hydration and supporting overall health.
-
Heart Health:
-
-
- The fruit’s potassium content is beneficial for heart health by helping regulate blood pressure.
-
Blood Sugar Control:
-
- Dragon fruit may have a positive impact on blood sugar levels due to its fiber content and low glycemic index.
Incorporating Dragon Fruit into Your Diet:
With its sweet and refreshing flavor, dragon fruit can be enjoyed in various ways. Here are some delicious ways to incorporate dragon fruit into your diet:
Fresh and Sliced:
-
-
- Enjoy dragon fruit on its own by slicing it into wedges for a simple and refreshing snack.
-
Smoothie Bowls:
-
-
- Add dragon fruit to smoothie bowls for a burst of color, flavor, and nutritional benefits.
-
Fruit Salads:
-
-
- Include dragon fruit in fruit salads to elevate the visual appeal and taste of the dish.
-
Juices and Beverages:
-
-
- Blend dragon fruit into juices, smoothies, or even cocktails for a tropical twist.
-
Desserts:
-
- Incorporate dragon fruit into desserts such as sorbets, ice creams, or fruit tarts.
Conclusion:
Dragon fruit’s popularity continues to soar, thanks to its unique appearance, delightful taste, and impressive health benefits. Understanding the factors influencing its seasonality, the varieties available, and cultivation practices provides valuable insights for both consumers and those involved in the dragon fruit industry.
Whether you’re enjoying dragon fruit in a tropical paradise, a subtropical region, or a greenhouse in a colder climate, the beauty of this exotic fruit lies in its versatility and adaptability. So, the next time you savor the vibrant flavors of dragon fruit, take a moment to appreciate the journey it took from cultivation to your plate, and relish in the delightful experience that is dragon fruit season.